

Intellectual debate has also focused on whether ethnic conflict has become more prevalent since the end of the Cold War, and on devising ways of managing conflicts, through instruments such as consociationalism and federalisation.
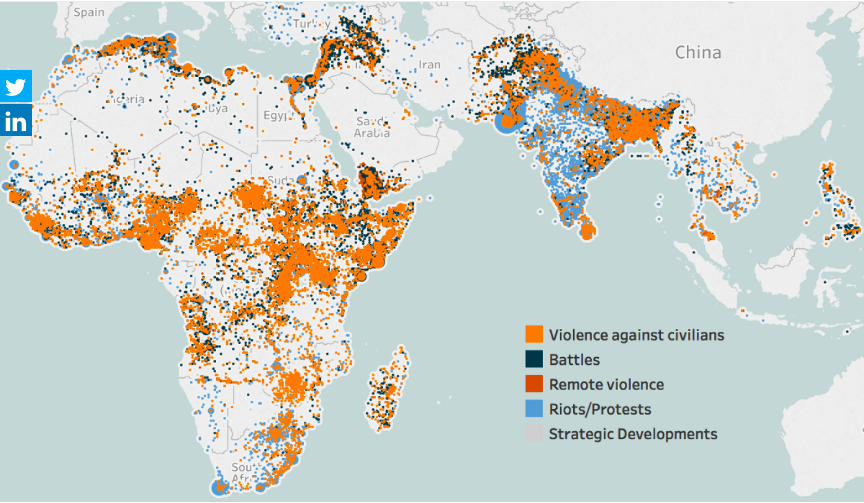
Recently, some have argued for either top-down or bottom-up explanations for ethnic conflict. Īcademic explanations of ethnic conflict generally fall into one of three schools of thought: primordialist, instrumentalist or constructivist. This criterion differentiates ethnic conflict from other forms of struggle.

While the source of the conflict may be political, social, economic or religious, the individuals in conflict must expressly fight for their ethnic group's position within society. An ethnic conflict is a conflict between two or more ethnic groups.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
